Hail
Data Limitations
Hail data are not of sufficient quality to robustly determine historical trends and is of poorer quality than even the tornado dataset. This can be attributed to the increases in non-meteorological factors such as population and storm spotter coverage over time, as well as the uncertainty in reported hail size. However, the recent acknowledgement to assess the number of hail days instead of individual hail reports has mitigated some of the biases.
Definition and Description
Showery precipitation in the form of irregular pellets or balls of ice more than 5mm (0.2 inches) in diameter, falling from a cumulonimbus cloud (NWS 2009).
Hail forms by the collision of supercooled drops – raindrops that are still liquid even though the air around them is below freezing. The hailstone grows, supported by the updraft, until it is too heavy to remain aloft. Stronger updrafts generally produce larger hail size. Because obtaining large hail sizes requires a strong updraft, the timing of large hail is related to the lifecycle of large cumulonimbus clouds, which peak in intensity during late afternoon and evening hours. Updrafts may also be supported by vertical motion along a boundary, such as a front or mountains.
Hail severity is rated by the diameter of the largest hailstones in a storm. Hail of 1-inch diameter or greater is considered severe.
Historical Data
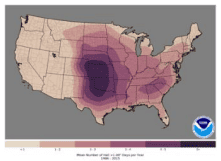
Severe Hail Days Per Year
(1986-2015) NOAA/National Weather Service Storm Prediction CenterThis map shows the average number of days per year in which severe hail reports occurred in the specified area during the period noted. The map provides a sense of the approximate number of days each year that you can expect to see severe (0.75- and 1-inch) or significant (greater than 2-inch) hail in your area. Note: Severe hail size changed from 0.75” to 1” in 2009, so both sizes are included on the webpage.
1. Scroll down and click on Hail Climatology – New Severe Hail (Greater Than 1.00” or Greater Than 2.00”) to view the full-size image.
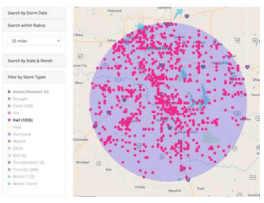
Severe Hail Reports
Hail: (1955-present) Southern Regional Climate CenterThis interactive tool shows you the historical record for individual severe hail reports in your area. It can be used to determine hail events that have impacted your area or close to your area.
1. On left side of screen, click on Search with Radius. 2. Choose the diameter of the area of which you want to investigate (25 or 50 miles). 3. Select Hail (de-select Tornado and Wind). 4. Pan, zoom, and then click on the map area of interest. 5. Reports are displayed on the map and in two tables below the map.
Map: Mouse over individual storm reports for details.
Tables: There are two tables, Recent Storm Data and Historical Storm Data. Click on column header to sort by column of interest. For example, to view the dates in which the largest hail occurred, click on the Scale column headers to sort by the largest hail values.
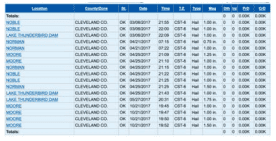
Storm Events Database
Hail: (1955-present)NOAA National Centers for Environmental InformationThis interactive tool shows you the historical record for individual severe hail reports by county. It can be used to determine hail events that have impacted your area or close to your area.
1. On the bottom left, under Select State or Area, choose Oklahoma → then Search 2. From top to bottom, select a specific Begin and End Date, as well as County of interest. 3. Under Event Type(s), select Hail. 4. Under Advanced Search and Filter Options → Hail Filter, select hail size of interest. 5. Press Search. Summary results are presented in a table. Note: This tool can be used to analyze a variety of additional hazards with various time periods, and hail data goes as far back as 1955.
Climate Change Trends
Hail is commonly associated with severe thunderstorms. Climate models project an increase in the frequency and intensity of severe thunderstorms, and events with large hail are projected to increase (Kossin et al. 2017). At the same time, models project an overall decrease in the number of days with hail per year (Brimelow et al. 2017). Confidence in the projections is currently low, however, due to the isolated and sporadic nature of hail events and limited comprehensive datasets which make it difficult to track long-term trends (Wuebbles et al. 2017a).